2.10.1. Docker client ¶
The docker client is very simple, and we can enter the docker command directly to see all the command options for the Docker client.
runoob@runoob:~# docker
You can use the command docker command –help Learn more about the use of the specified Docker command.
For example, we want to check docker stats How to use the instruction:
runoob@runoob:~# docker stats --help
2.10.2. Container use ¶
Get the image ¶
If we do not have a ubuntu image locally, we can use the docker pull command to load the ubuntu image:
$ docker pull ubuntu
Start the container ¶
The following command starts a container using the ubuntu image, and the parameter is to enter the container in command-line mode:
$ docker run -it ubuntu /bin/bash

Parameter description:
-i Interactive operation
-t Terminal.
ubuntu : ubuntu image.
/bin/bash Put after the image name is the command, here we want to have an interactive Shell, so we use / bin/bash.
To exit the terminal, type directly exit :
root@ed09e4490c57:/# exit

Start a container that has stopped running ¶
The command to view all containers is as follows:
$ docker ps -a
Click on the picture to see the larger picture:
` <../wp-content/uploads/2016/05/docker-container-psa.png>` __
Start a stopped container using docker start:
$ docker start b750bbbcfd88

Background operation ¶
In most scenarios, we want the docker service to run in the background, and we can specify the operation mode of the container via-d.
$ docker run -itd --name ubuntu-test ubuntu /bin/bash
Click on the picture to see the larger picture:
` <../wp-content/uploads/2016/05/docker-run-d.png>` __
` <../wp-content/uploads/2016/05/docker-run-d2.png>` __
注: Adding the-d parameter will not enter the container by default, and you need to use instructions to enter the container. docker exec (described below).
Stop a container ¶
The command to stop the container is as follows:
$ docker stop <容器 ID>

The stopped container can be restarted via docker restart:
$ docker restart <容器 ID>

Enter the container ¶
In use -d Parameter, the container will enter the background after startup. If you want to enter the container at this point, you can enter it by using the following command:
docker attach
docker exec It is recommended that you use the docker exec command, because this exit from the container terminal will not cause the container to stop.
attach 命令
The use of the docker attach command is demonstrated below.
$ docker attach 1e560fca3906
` <../wp-content/uploads/2016/05/docker-attach.png>` __
注意: If you exit from this container, it will cause the container to stop.
exec 命令
The use of the docker exec command is demonstrated below.
docker exec -it 243c32535da7 /bin/bash
` <../wp-content/uploads/2016/05/docker-exec.png>` __
注意: If you exit from this container, the container will not stop, which is why it is recommended to use the docker exec The reason.
For more parameter instructions, use the docker exec– help command.
Export and import containers ¶
导出容器
If you want to export a local container, you can use docker export Orders.
$ docker export 1e560fca3906 > ubuntu.tar
Export the container 1e560fca3906 snapshot to the local file ubuntu.tar.
` <../wp-content/uploads/2016/05/docker-export.png>` _ _ this snapshots the export container to the local file.
导入容器快照
You can use docker import to import as a mirror from the container snapshot file. The following example imports the snapshot file ubuntu.tar into the mirror test/ubuntu:v1:
$ cat docker/ubuntu.tar | docker import - test/ubuntu:v1
` <../wp-content/uploads/2016/05/docker-import.png>` _ _ in addition, you can also import by specifying URL or a directory, for example:
$ docker import http://example.com/exampleimage.tgz example/imagerepo
Delete Container ¶
Delete container usage docker rm Command:
$ docker rm -f 1e560fca3906
` <../wp-content/uploads/2016/05/docker-container-rmi.png>` The following command cleans up all containers that are in a terminated state.
$docker container prune
2.10.3. Run a web application ¶
The container we ran earlier is of no particular use.
Next let’s try to build a web application using docker.
We will run a Python Flask application in the docker container to run a web application.
runoob@runoob:~# docker pull training/webapp # 载入镜像
runoob@runoob:~# docker run -d -P training/webapp python app.py

Parameter description:
-d: Let the container run in the background.
-P: Randomly map the network ports used inside the container to the hosts we use.
2.10.4. View the WEB application container ¶
Use docker ps to see the container we are running:
runoob@runoob:~# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND ... PORTS
d3d5e39ed9d3 training/webapp "python app.py" ... 0.0.0.0:32769->5000/tcp
There is more port information here.
PORTS
0.0.0.0:32769->5000/tcp
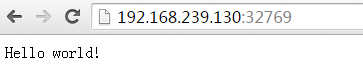
Docker opens port 5000 (the default Python Flask port) to map to host port 32769.
At this time, we can access the WEB application through the browser.
We can also set different ports with the-p parameter:
runoob@runoob:~$ docker run -d -p 5000:5000 training/webapp python app.py
docker ps View running containers
runoob@runoob:~# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE PORTS NAMES
bf08b7f2cd89 training/webapp ... 0.0.0.0:5000->5000/tcp wizardly_chandrasekhar
d3d5e39ed9d3 training/webapp ... 0.0.0.0:32769->5000/tcp xenodochial_hoov
Port 5000 inside the container is mapped to port 5000 on our local host.
2.10.5. Shortcuts to network ports ¶
Pass through docker ps Command to see the port mapping of the container docker Another shortcut is also provided docker port , using the docker port You can check the port number of the specified (ID or name) container that maps to the host.
The web application container ID we created above is bf08b7f2cd89 The name is wizardly_chandrasekhar .
I can use docker port bf08b7f2cd89 or docker port wizardly_chandrasekhar to see how the container ports are mapped.
runoob@runoob:~$ docker port bf08b7f2cd89
5000/tcp -> 0.0.0.0:5000
runoob@runoob:~$ docker port wizardly_chandrasekhar
5000/tcp -> 0.0.0.0:5000
2.10.6. View the WEB application log ¶
Docker logs [ID或者名字] You can view the standard output inside the container.
runoob@runoob:~$ docker logs -f bf08b7f2cd89
* Running on http://0.0.0.0:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
192.168.239.1 - - [09/May/2016 16:30:37] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 -
192.168.239.1 - - [09/May/2016 16:30:37] "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 -
-f: Let docker logs Like using tail -f The standard output inside the container is also output.
From the above, we can see that the application uses port 5000 and can see the application’s access log.
2.10.7. View the process of the WEB application container ¶
We can also use docker top to view the processes running inside the container
runoob@runoob:~$ docker top wizardly_chandrasekhar
UID PID PPID ... TIME CMD
root 23245 23228 ... 00:00:00 python app.py
2.10.8. Check the WEB application ¶
Use docker inspect To view the underlying information of Docker. It returns a JSON file that records the configuration and status information of the Docker container.
runoob@runoob:~$ docker inspect wizardly_chandrasekhar
[
{
"Id": "bf08b7f2cd897b5964943134aa6d373e355c286db9b9885b1f60b6e8f82b2b85",
"Created": "2018-09-17T01:41:26.174228707Z",
"Path": "python",
"Args": [
"app.py"
],
"State": {
"Status": "running",
"Running": true,
"Paused": false,
"Restarting": false,
"OOMKilled": false,
"Dead": false,
"Pid": 23245,
"ExitCode": 0,
"Error": "",
"StartedAt": "2018-09-17T01:41:26.494185806Z",
"FinishedAt": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z"
},
......
2.10.9. Stop the WEB application container ¶
runoob@runoob:~$ docker stop wizardly_chandrasekhar
wizardly_chandrasekhar
2.10.10. Restart the WEB application container ¶
For containers that have been stopped, we can use the command docker start to start.
runoob@runoob:~$ docker start wizardly_chandrasekhar
wizardly_chandrasekhar
Docker ps-l queries the last created container:
# docker ps -l
CONTAINER ID IMAGE PORTS NAMES
bf08b7f2cd89 training/webapp ... 0.0.0.0:5000->5000/tcp wizardly_chandrasekhar
For a running container, we can restart it using the docker restart command.
2.10.11. Remove the WEB application container ¶
We can use the docker rm command to delete unwanted containers
runoob@runoob:~$ docker rm wizardly_chandrasekhar
wizardly_chandrasekhar
When deleting a container, the container must be in a stopped state, otherwise the following error will be reported
runoob@runoob:~$ docker rm wizardly_chandrasekhar
Error response from daemon: You cannot remove a running container bf08b7f2cd897b5964943134aa6d373e355c286db9b9885b1f60b6e8f82b2b85. Stop the container before attempting removal or force remove