Factory pattern (Factory Pattern) is one of the most commonly used design patterns in Java. This type of design pattern is a creative pattern, which provides the best way to create objects.
In factory mode, we do not expose the creation logic to the client when we create the object, and we point to the newly created object by using a common interface. 意图: Define an interface to create an object and let its subclass decide which factory class to instantiate, and the factory pattern delays the creation process to the subclass. 主要解决: The main problem is to solve the problem of interface selection. 何时使用: We explicitly plan to create different instances under different conditions. 如何解决: Let its subclass implement the factory interface and return an abstract product. 关键代码: The creation process is performed in its subclass. 应用实例: 1. You need a car, and you can pick up the goods directly from the factory, regardless of how the car is made and the specific implementation of the car. 2. Hibernate only needs to change the dialect and driver to change the database. 优点: 1. If a caller wants to create an object, he only needs to know its name. 2. High expansibility. If you want to add a product, just extend a factory class. 3. Shielding the specific implementation of the product, the caller only cares about the interface of the product. 缺点: Each time a product is added, it is necessary to add a specific class and object implementation factory, which doubles the number of classes in the system, increases the complexity of the system to a certain extent, and increases the dependence of the specific classes of the system. This is not a good thing. 使用场景: 1, logger: records may be recorded to the local hard disk, system events, remote servers, etc., the user can choose where to record the log. 2, database access, when the user does not know which kind of database the final system uses, and the database may change. 3. To design a framework for connecting to the server, we need three protocols, “POP3”, “IMAP” and “HTTP”. We can take these three as product classes and implement an interface together. 注意事项: As a way to create a class pattern, you can use the factory method pattern wherever you need to generate complex objects. One thing to note is that complex objects are suitable for using factory patterns, while simple objects, especially those that can be created through new, do not need to use factory schemas. If you use the factory pattern, you need to introduce a factory class, which increases the complexity of the system. We will create a Shape Interface and implementation Shape The entity class of the interface. The next step is to define the factory class ShapeFactory . FactoryPatternDemo Class usage ShapeFactory To get Shape Object. It will be directed to ShapeFactory Pass the message ( CIRCLE / RECTANGLE / SQUARE To get the type of object it needs Create an interface: Create an entity class that implements the interface. Create a factory that generates objects of entity classes based on the given information. Using this factory, the object of the entity class is obtained by passing type information. Execute the program and output the result: 6.3.1. Introduction ¶
6.3.2. Realize ¶
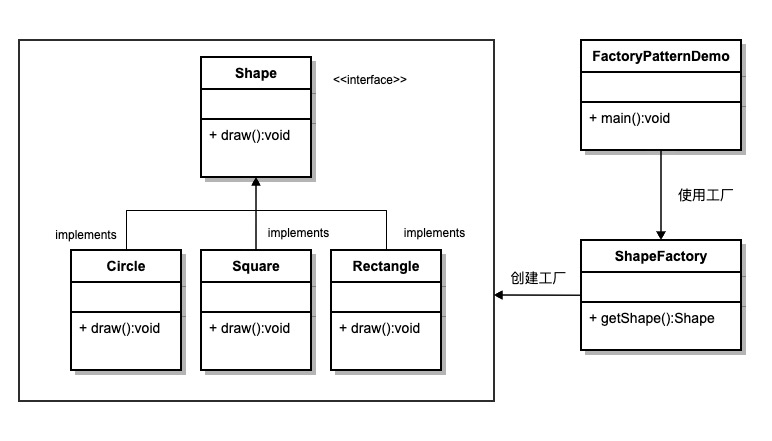
6.3.3. Step 1 ¶
Shape.java ¶
publicinterfaceShape{voiddraw();}
6.3.4. Step 2 ¶
Rectangle.java ¶
publicclassRectangleimplementsShape{@Overridepublicvoiddraw(){System.out.println("Inside
Rectangle::draw() method.");}}
Square.java ¶
publicclassSquareimplementsShape{@Overridepublicvoiddraw(){System.out.println("Inside
Square::draw() method.");}}
Circle.java ¶
publicclassCircleimplementsShape{@Overridepublicvoiddraw(){System.out.println("Inside
Circle::draw() method.");}}
6.3.5. Step 3 ¶
ShapeFactory.java ¶
publicclassShapeFactory{//使用 getShape
方法获取形状类型的对象publicShapegetShape(StringshapeType){if(shapeType==null){returnnull;}if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("CIRCLE")){returnnewCircle();}elseif(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("RECTANGLE")){returnnewRectangle();}elseif(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("SQUARE")){returnnewSquare();}returnnull;}}
6.3.6. Step 4 ¶
FactoryPatternDemo.java ¶
publicclassFactoryPatternDemo{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){ShapeFactoryshapeFactory=newShapeFactory();//获取
Circle 的对象,并调用它的 draw
方法Shapeshape1=shapeFactory.getShape("CIRCLE");//调用 Circle 的 draw
方法shape1.draw();//获取 Rectangle 的对象,并调用它的 draw
方法Shapeshape2=shapeFactory.getShape("RECTANGLE");//调用 Rectangle 的
draw 方法shape2.draw();//获取 Square 的对象,并调用它的 draw
方法Shapeshape3=shapeFactory.getShape("SQUARE");//调用 Square 的 draw
方法shape3.draw();}}
6.3.7. Step 5 ¶
Inside Circle::draw() method.
Inside Rectangle::draw() method.
Inside Square::draw() method.
6.3.8. Other related articles ¶