You need to read this chapter before you read it. Django 模型 Perform basic configuration and understand solutions to common problems.
Next, let’s recreate a project app01 (if it has been created before, ignore the following):
django-admin.py startproject app01
Next, find the INSTALLED_APPS item in settings.py, as follows:
INSTALLED_APPS = (
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'app01', # 添加此项
)
Next, tell Django to connect to the mysql database using the pymysql module: Add the following classes to the models.py in the project: Then execute the following command on the command line: If you execute the above command, the following error message appears: The reason is that MySQLclient only supports Python3.4, so if you use a later version of python, you need to modify it as follows: 通过报错信息的文件路径找到 …site-packagesDjango-2.0-py3.6.eggdjangodbbackendsmysql 这个路径里的 base.py 文件,把这两行代码注释掉(代码在文件开头部分): In general, the code file path information of the error report will automatically jump to the number of lines in the error file, and at this time we comment out the number of code lines reported. At this point, the database runoob creates a table of app01_book. Next, we add the views.py and models.py files, the app01 project directory structure, to the app01 project: Rule configuration: 方式一: Model class instantiates objects To import the models.py file from the app directory: And the object .save () must be executed after the object is instantiated in order to add successfully in the database. 方式二: Implemented through the method create provided by objects provided by ORM (recommended) Use all() Method to query everything. What is returned is the QuerySet type data, similar to list, in which there are objects of the model class, and the objects of the model class can be fetched with the index subscript. filter() Method is used to query data that meets the criteria. What is returned is the QuerySet type data, similar to list, which contains the objects of the model class that meet the conditions, and the objects of the model class can be fetched with the index subscript. Pk=3 means the primary key primary key=3, which is equivalent to id=3. Because id has a special meaning in pycharm, it is a built-in function id () that looks at the memory address, so it uses competition. exclude() Method is used to query data that does not meet the criteria. What is returned is the QuerySet type data, which is similar to list, in which there are objects of the model class that do not meet the conditions, and the objects of the model class can be fetched with the index subscript. get() Method is used to query eligible objects that return model classes. There can be only one qualified object, and an error will be thrown if there are more than one or none of the objects that meet the filter criteria. order_by() Method is used to sort query results. What is returned is the QuerySet type data, similar to list, in which the objects of the sorted model class are put, and the objects of the model class can be fetched with the index subscript. 注意: a、参数的字段名要加引号。 b、降序为在字段前面加个负号 -。 reverse() Method is used to reverse the query results. What is returned is the QuerySe t type data, similar to list, which contains the objects of the inverted model class, and the objects of the model class can be fetched with the index subscript. count() Method is used to query the amount of data returned is an integer. first() Method returns the first piece of data, the data returned is the object of the model class, and the index subscript can also be used. [0] . The last piece of data returned by the last () method is that the object of the model class cannot be indexed. [-1] ORM does not have a reverse index exists() Method is used to determine whether there is data in the QuerySet list of the results of the query. The data type returned is Boolean, true, not false. 注意: The judged data type can only be QuerySet type data, not an object of integer and model class. values() Method is used to query the data of some fields. What is returned is QuerySet type data, similar to list, which is not an object of the model class, but an iterative dictionary sequence in which the key is the field and the value is the data. 注意: Quote the field name of the parameter Want the field name and data to use values values_list() Method is used to query the data of some fields. What is returned is the QuerySet type data, which is similar to list, in which there are not objects of the model class, but tuples, and the tuples contain the data corresponding to the query fields. 注意: Quote the field name of the parameter Just want the data to use values_list distinct() Method is used to deduplicate the data. QuerySet type data is returned. 注意: There is no point in duplicating the objects of the model class, because each object is a different existence. Distinct () is generally used in conjunction with values or values_list. filter() The method is based on fuzzy query with double underscore (exclude synonym). 注意: In filter, you can only use the equal sign =, not the greater than sign >, the less than sign <, and so on. _ _ in is used to read the interval, followed by a list after the = sign. __gt The greater than sign, followed by a number after the = sign. __gte Greater than or equal to, followed by a number. 7.11.1. Example ¶
# 在与 settings.py 同级目录下的 \__init__.py 中引入模块和进行配置
import pymysql
pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()
Create a model ¶
7.11.2. app01/models.py ¶
class Book(models.Model):
id = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) # id 会自动创建,可以手动写入
title = models.CharField(max_length=32) # 书籍名称
price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=5, decimal_places=2) #
书籍价格
publish = models.CharField(max_length=32) # 出版社名称
pub_date = models.DateField() # 出版时间
$ python3 manage.py migrate # 创建表结构
$ python3 manage.py makemigrations app01 # 让 Django 知道我们在我们的模型有一些变更
$ python3 manage.py migrate app01 # 创建表结构
Common error message ¶

if version < (1, 3, 13):
raise ImproperlyConfigured('mysqlclient 1.3.13 or newer is required; you have %s.' % Database.__version__)

app01
|-- app01
| |-- __init__.py
| |-- __pycache__
| |-- asgi.py
| |-- migrations
| |-- models.py
| |-- settings.py
| |-- urls.py
| |-- views.py
| `-- wsgi.py
Database addition ¶
7.11.3. App01/urls.py: file code: ¶
fromdjango.contribimportadminfromdjango.urlsimportpathfrom.importviewsurlpatterns=[path('add_book/',views.add_book),]
from app 目录 import models
7.11.4. App01/views.py: file code: ¶
fromdjango.shortcutsimportrender,HttpResponsefromapp01importmodelsdefadd_book(request):book=models.Book(title="菜鸟教程",price=300,publish="菜鸟出版社",pub_date="2008-8-8")book.save()returnHttpResponse("<p>数据添加成功!</p>")

7.11.5. App01/views.py: file code: ¶
fromdjango.shortcutsimportrender,HttpResponsefromapp01importmodelsdefadd_book(request):books=models.Book.objects.create(title="如来神掌",price=200,publish="功夫出版社",pub_date="2010-10-10")print(books,type(books))#
Book object (18)returnHttpResponse("<p>数据添加成功!</p>")

Find ¶
7.11.6. App01/views.py: file code: ¶
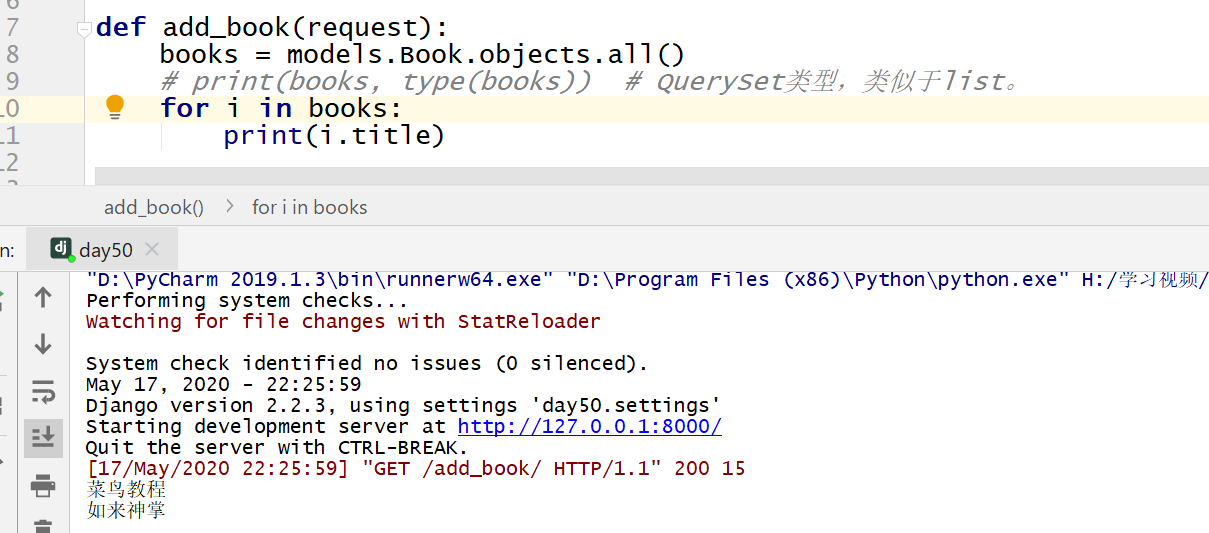
fromdjango.shortcutsimportrender,HttpResponsefromapp01importmodelsdefadd_book(request):books=models.Book.objects.all()print(books,type(books))#
QuerySet类型,类似于list,访问 url
时数据显示在命令行窗口中。returnHttpResponse("<p>查找成功!</p>")

7.11.7. App01/views.py: file code: ¶
fromdjango.shortcutsimportrender,HttpResponsefromapp01importmodelsdefadd_book(request):books=models.Book.objects.filter(pk=5)print(books)print("//////////////////////////////////////")books=models.Book.objects.filter(publish='菜鸟出版社',price=300)print(books,type(books))#
QuerySet类型,类似于list。returnHttpResponse("<p>查找成功!</p>")

7.11.8. App01/views.py: file code: ¶
fromdjango.shortcutsimportrender,HttpResponsefromapp01importmodelsdefadd_book(request):books=models.Book.objects.exclude(pk=5)print(books)print("//////////////////////////////////////")books=models.Book.objects.exclude(publish='菜鸟出版社',price=300)print(books,type(books))#
QuerySet类型,类似于list。returnHttpResponse("<p>查找成功!</p>")

7.11.9. App01/views.py: file code: ¶
fromdjango.shortcutsimportrender,HttpResponsefromapp01importmodelsdefadd_book(request):books=models.Book.objects.get(pk=5)books=models.Book.objects.get(pk=18)#
报错,没有符合条件的对象books=models.Book.objects.get(price=200)#
报错,符合条件的对象超过一个print(books,type(books))#
模型类的对象returnHttpResponse("<p>查找成功!</p>")

7.11.10. App01/views.py: file code: ¶
fromdjango.shortcutsimportrender,HttpResponsefromapp01importmodelsdefadd_book(request):books=models.Book.objects.order_by("price")#
查询所有,按照价格升序排列books=models.Book.objects.order_by("-price")#
查询所有,按照价格降序排列returnHttpResponse("<p>查找成功!</p>")

7.11.11. App01/views.py: file code: ¶
fromdjango.shortcutsimportrender,HttpResponsefromapp01importmodelsdefadd_book(request):#
按照价格升序排列:降序再反转books=models.Book.objects.order_by("-price").reverse()returnHttpResponse("<p>查找成功!</p>")

7.11.12. App01/views.py: file code: ¶
fromdjango.shortcutsimportrender,HttpResponsefromapp01importmodelsdefadd_book(request):books=models.Book.objects.count()#
查询所有数据的数量books=models.Book.objects.filter(price=200).count()#
查询符合条件数据的数量returnHttpResponse("<p>查找成功!</p>")

7.11.13. App01/views.py: file code: ¶
fromdjango.shortcutsimportrender,HttpResponsefromapp01importmodelsdefadd_book(request):books=models.Book.objects.first()#
返回所有数据的第一条数据returnHttpResponse("<p>查找成功!</p>")

7.11.14. App01/views.py: file code: ¶
fromdjango.shortcutsimportrender,HttpResponsefromapp01importmodelsdefadd_book(request):books=models.Book.objects.last()#
返回所有数据的最后一条数据returnHttpResponse("<p>查找成功!</p>")

7.11.15. Example ¶
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from app01 import models
def add_book(request):
books = models.Book.objects.exists()
# 报错,判断的数据类型只能为QuerySet类型数据,不能为整型
books = models.Book.objects.count().exists()
# 报错,判断的数据类型只能为QuerySet类型数据,不能为模型类对象
books = models.Book.objects.first().exists()
return HttpResponse("<p>查找成功!</p>")

7.11.16. Example ¶
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from app01 import models
def add_book(request):
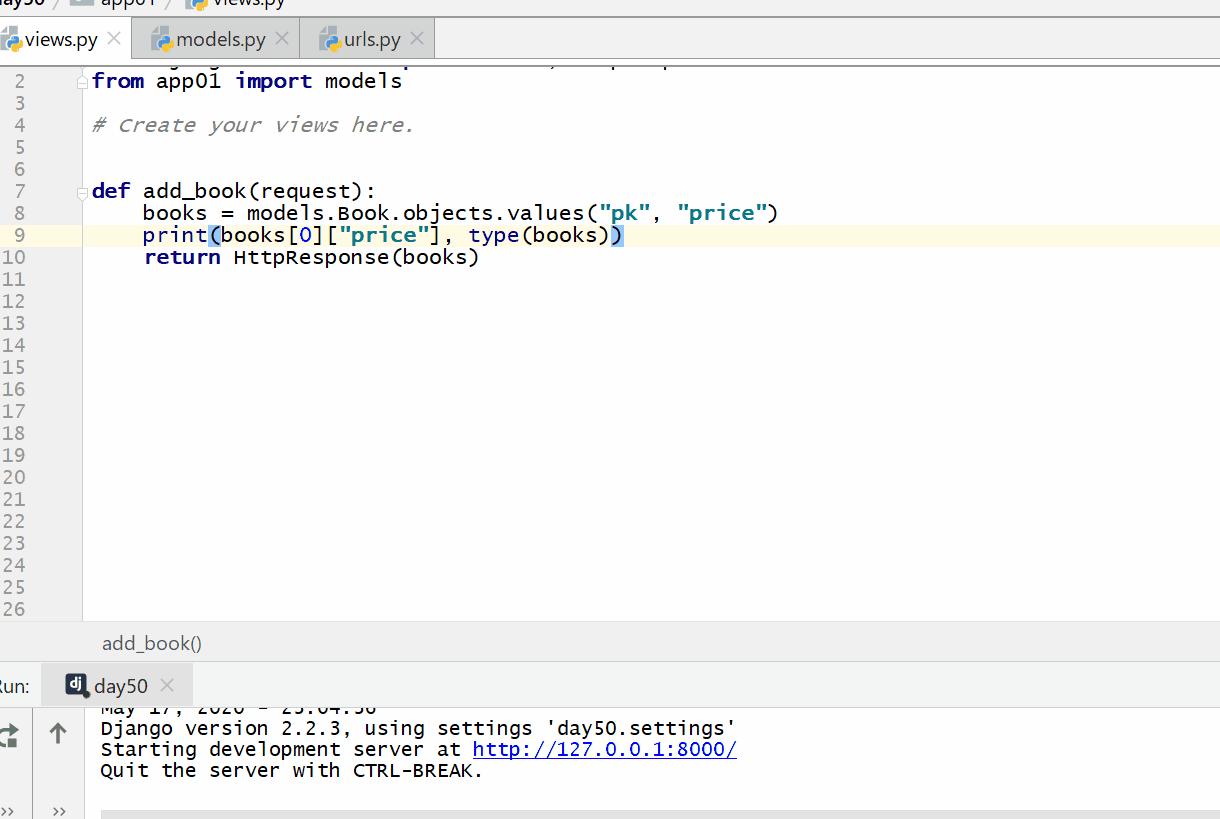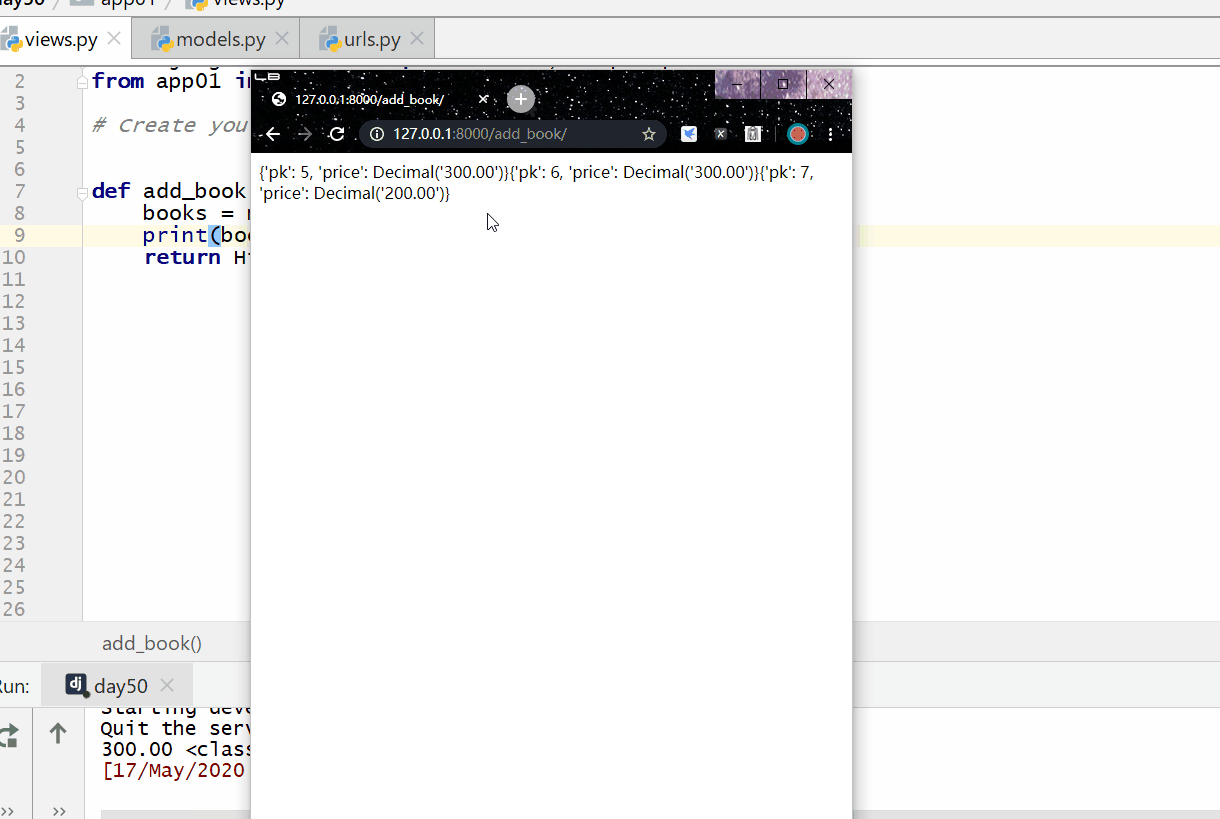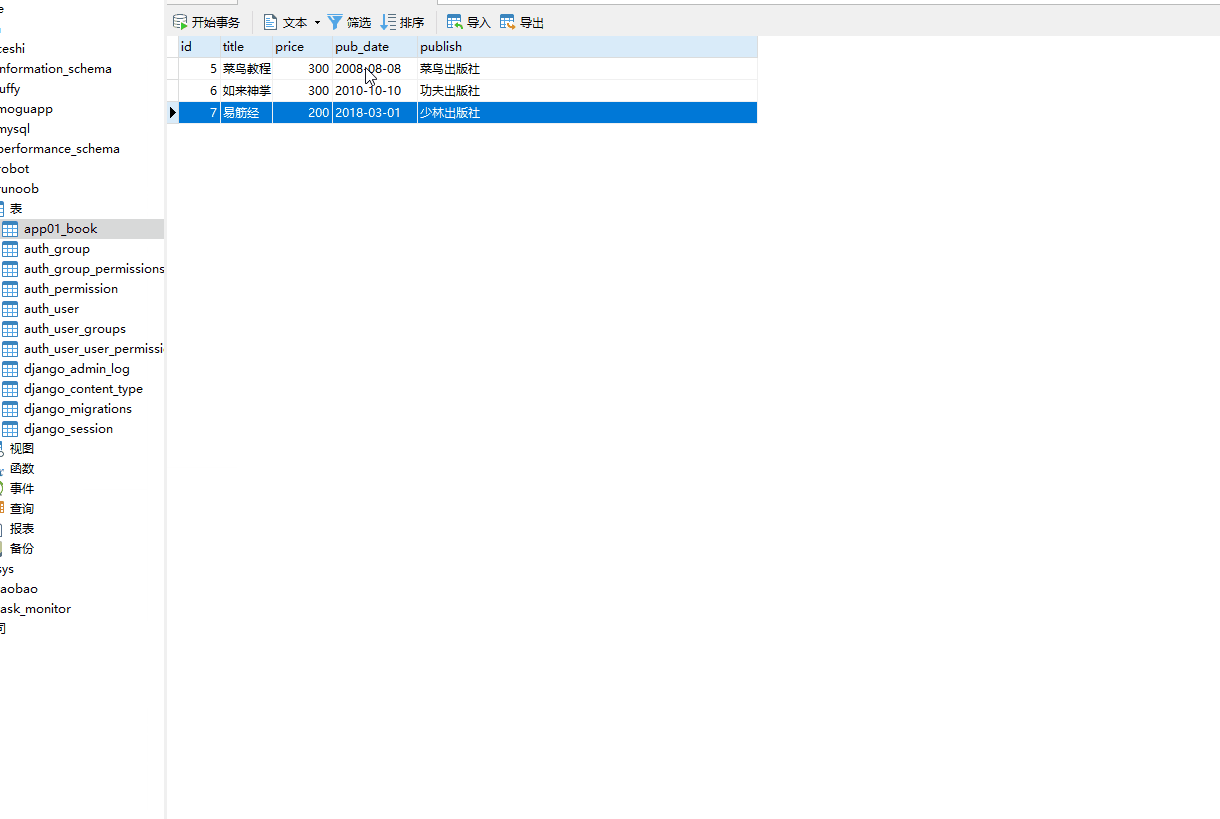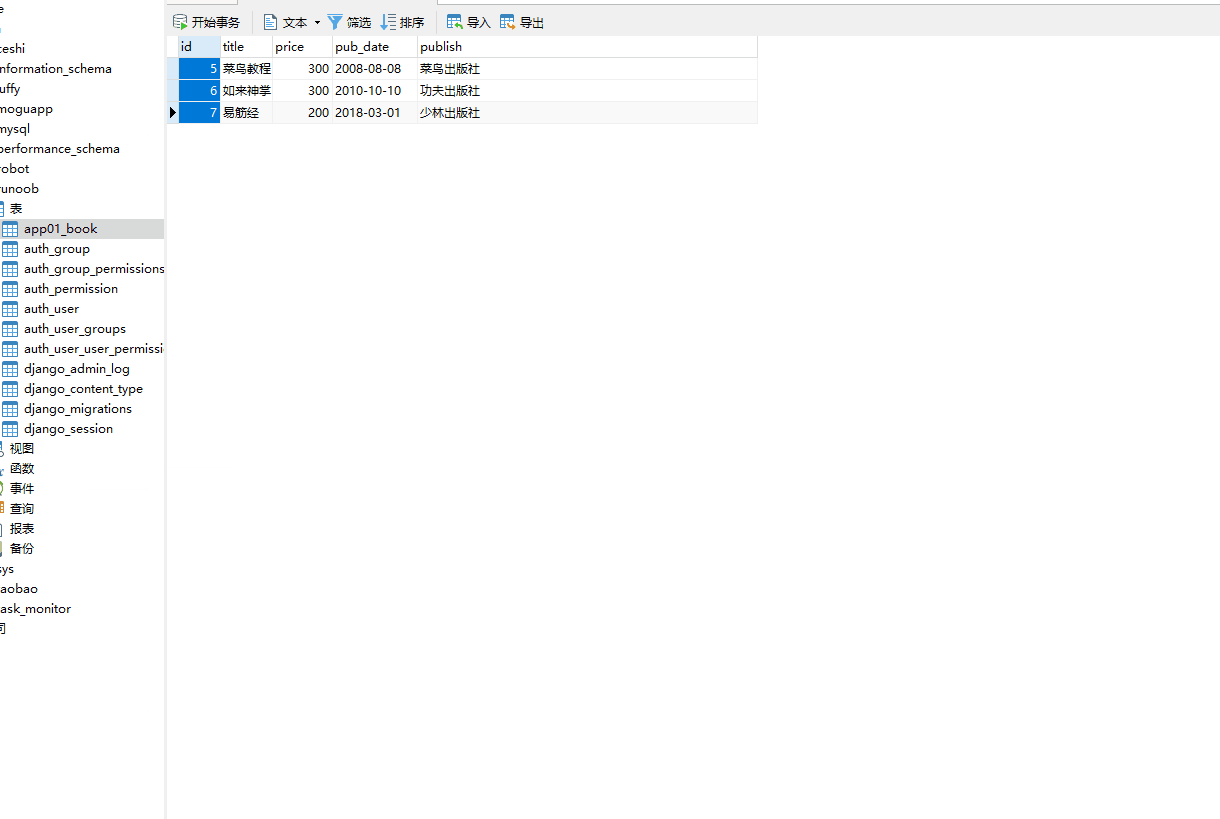
# 查询所有的id字段和price字段的数据
books = models.Book.objects.values("pk","price")
print(books[0]["price"],type(books)) #
得到的是第一条记录的price字段的数据
return HttpResponse("<p>查找成功!</p>")
7.11.17. Example ¶
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from app01 import models
def add_book(request):
# 查询所有的price字段和publish字段的数据
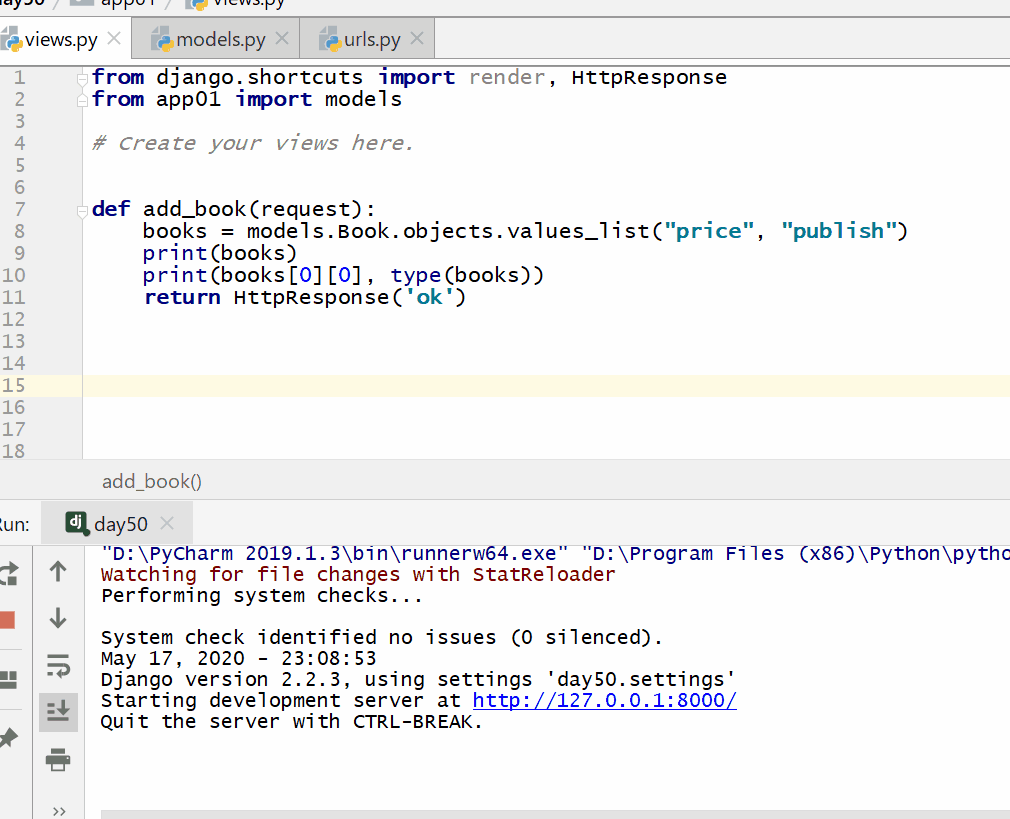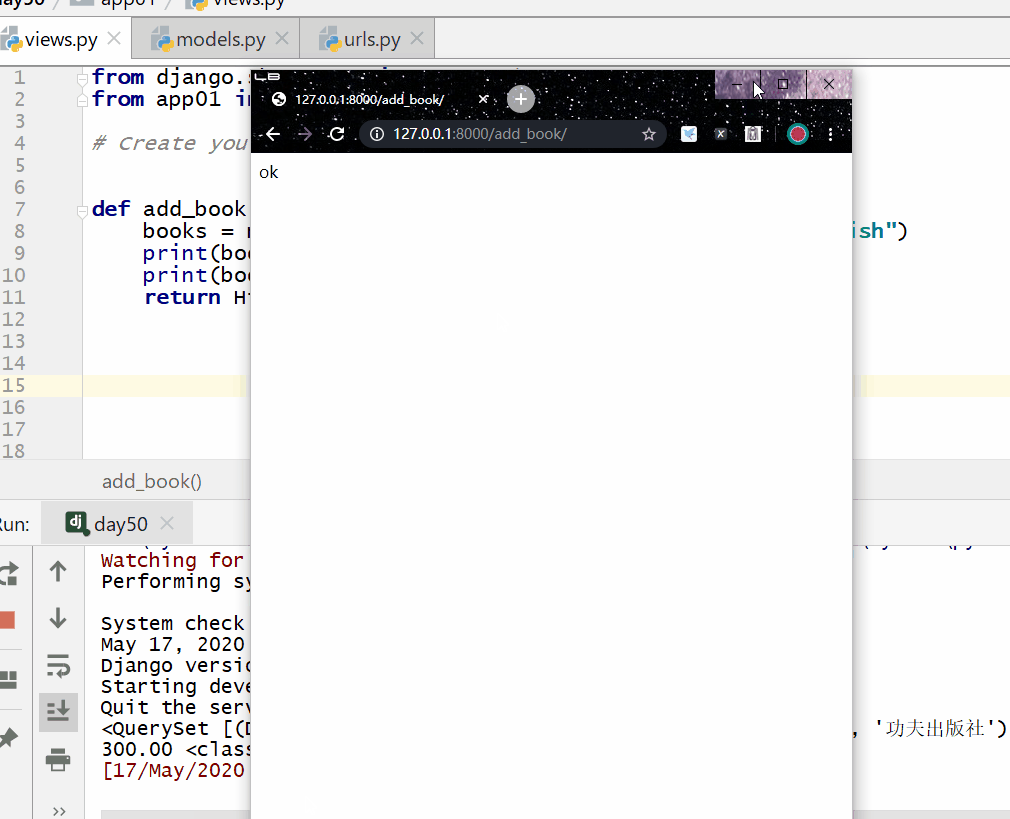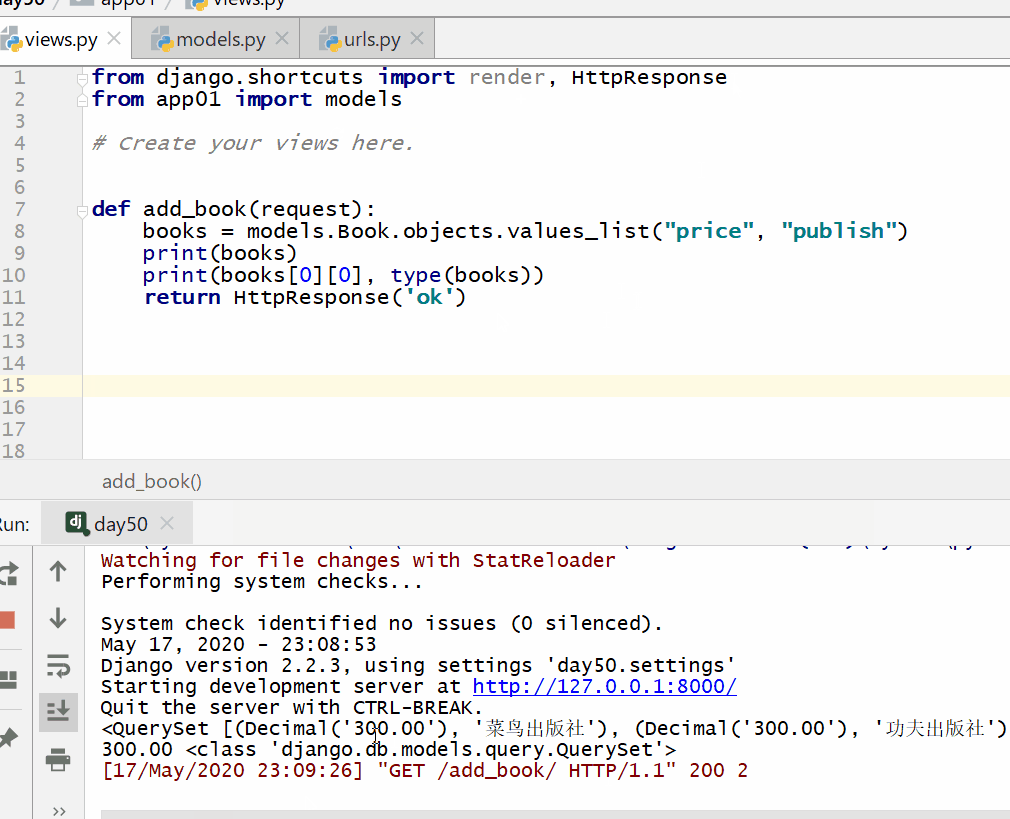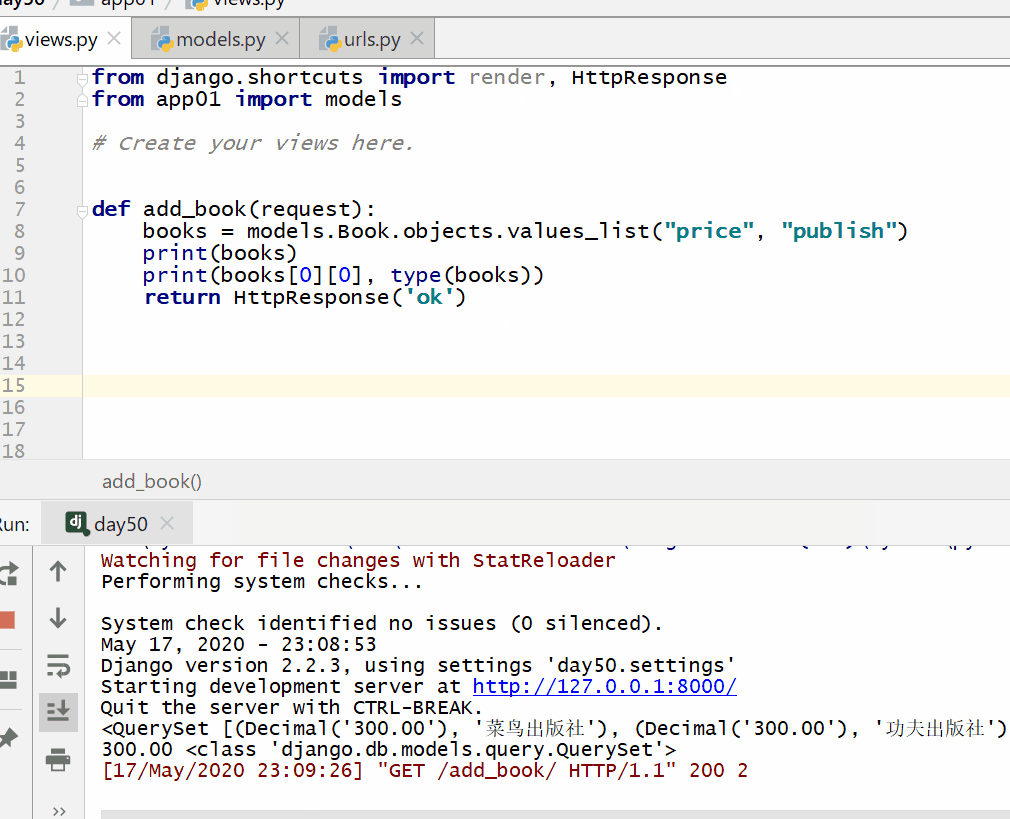
books = models.Book.objects.values_list("price","publish")
print(books)
print(books[0][0],type(books)) #
得到的是第一条记录的price字段的数据
return HttpResponse("<p>查找成功!</p>")
7.11.18. Example ¶
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from app01 import models
def add_book(request):
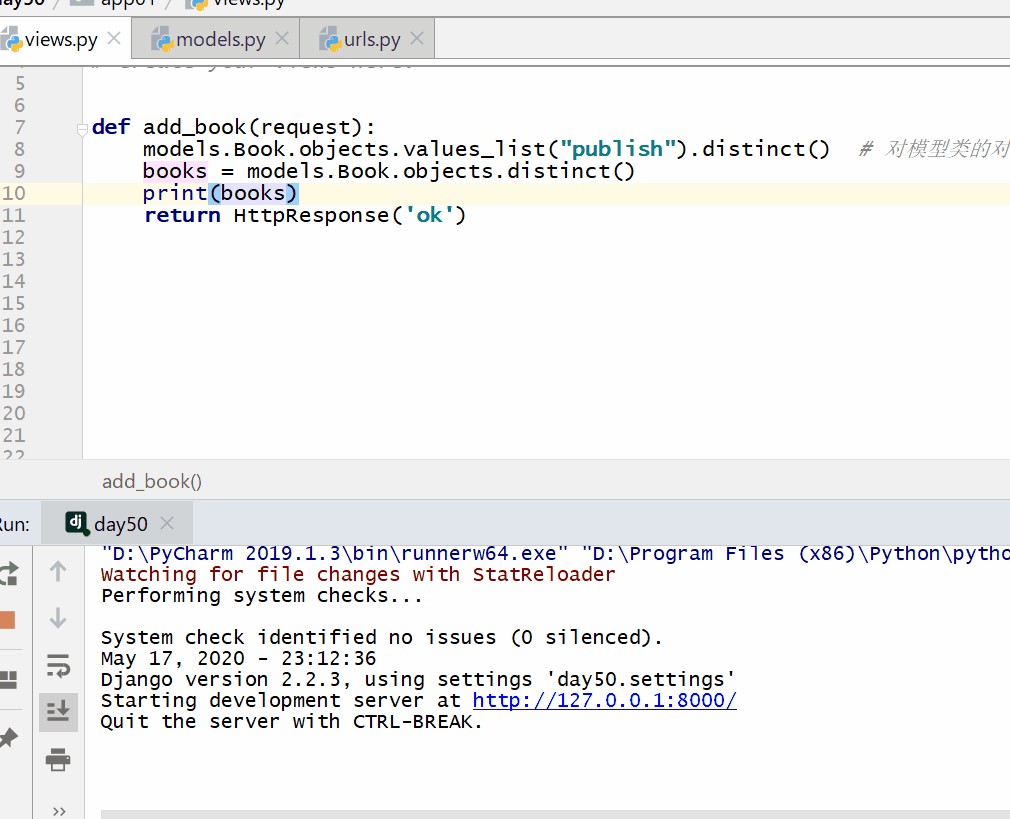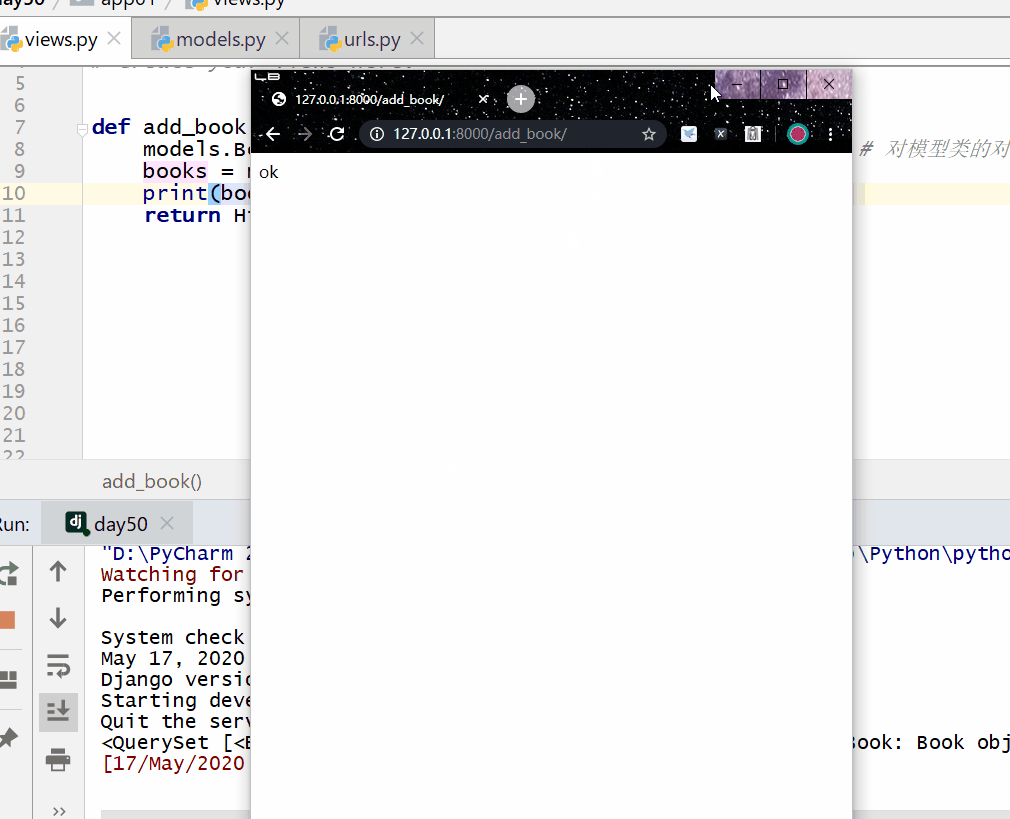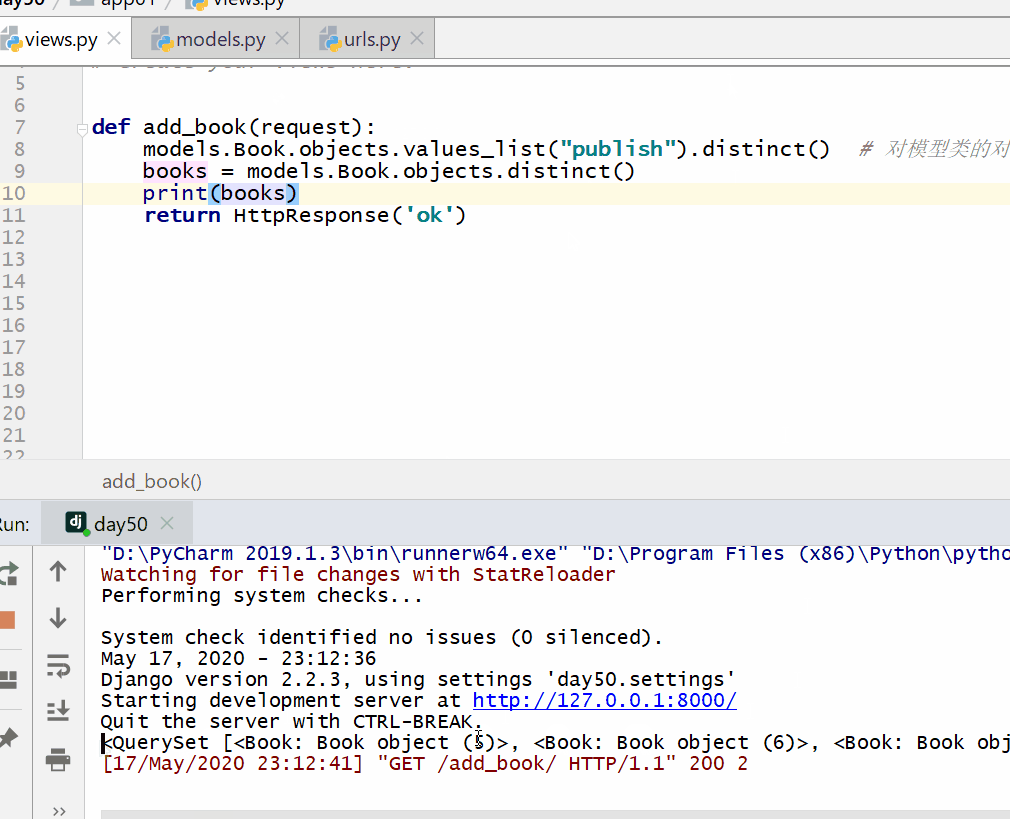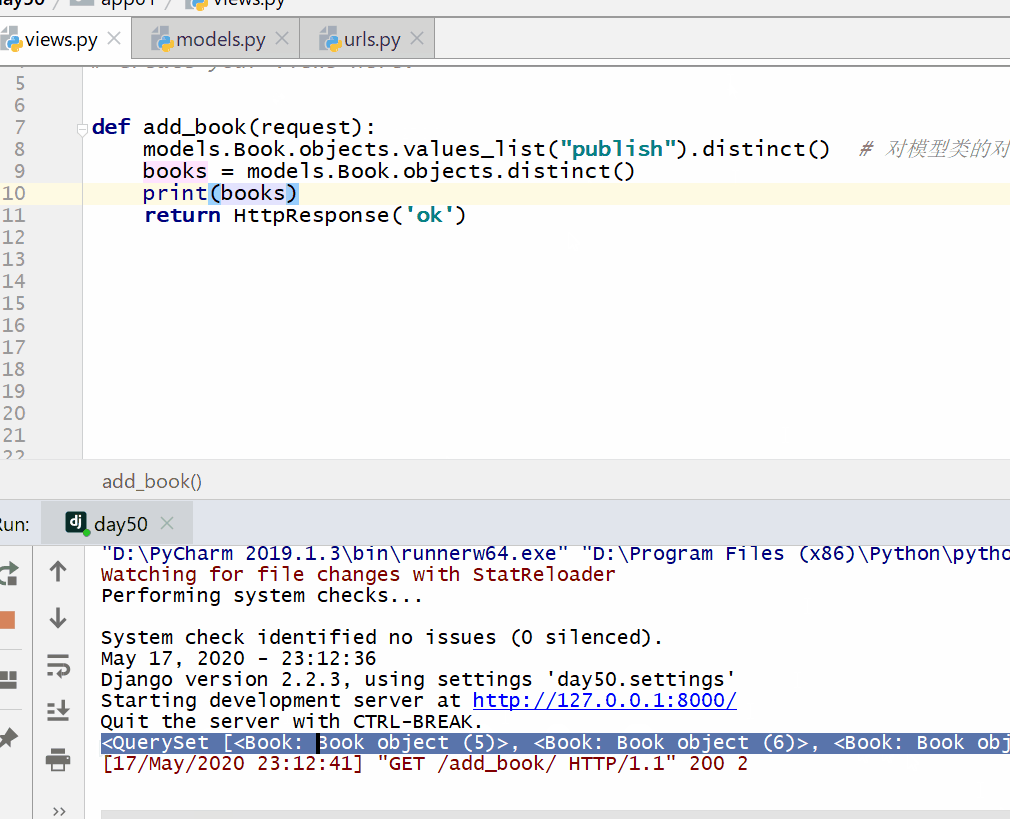
# 查询一共有多少个出版社
books = models.Book.objects.values_list("publish").distinct() #
对模型类的对象去重没有意义,因为每个对象都是一个不一样的存在。
books = models.Book.objects.distinct()
return HttpResponse("<p>查找成功!</p>")
7.11.19. Example ¶
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from app01 import models
def add_book(request):
# 查询价格为200或者300的数据
books = models.Book.objects.filter(price__in=[200,300])
return HttpResponse("<p>查找成功!</p>")

# 查询价格大于200的数据
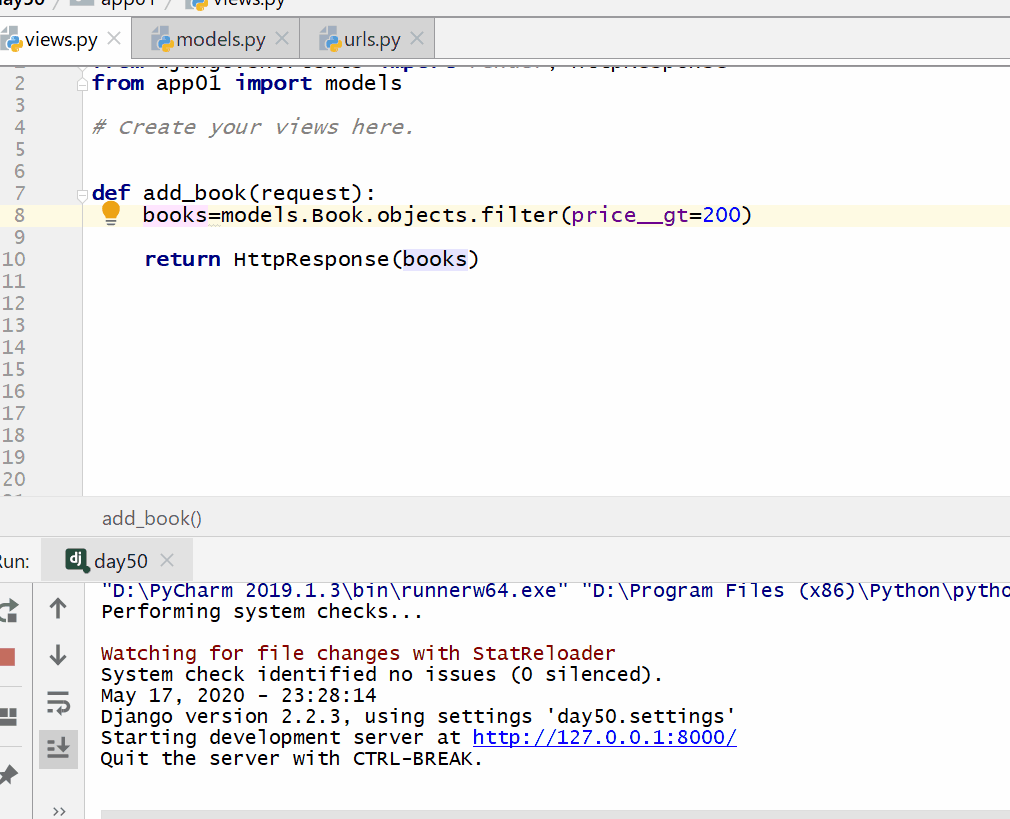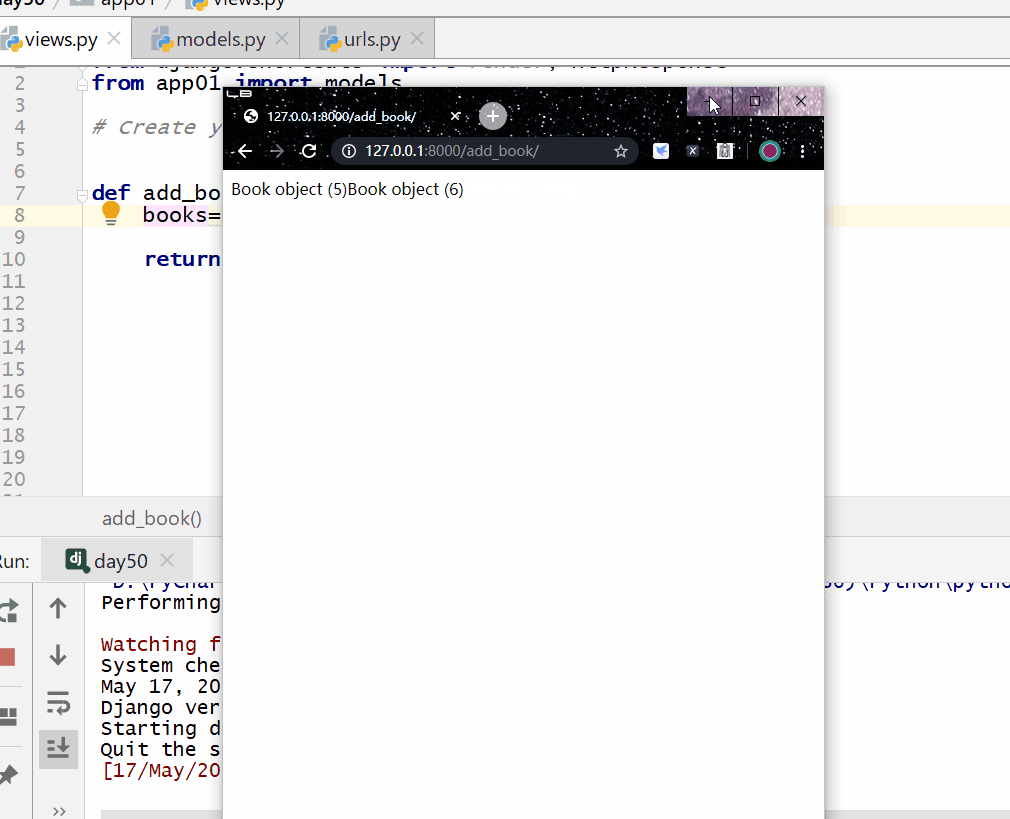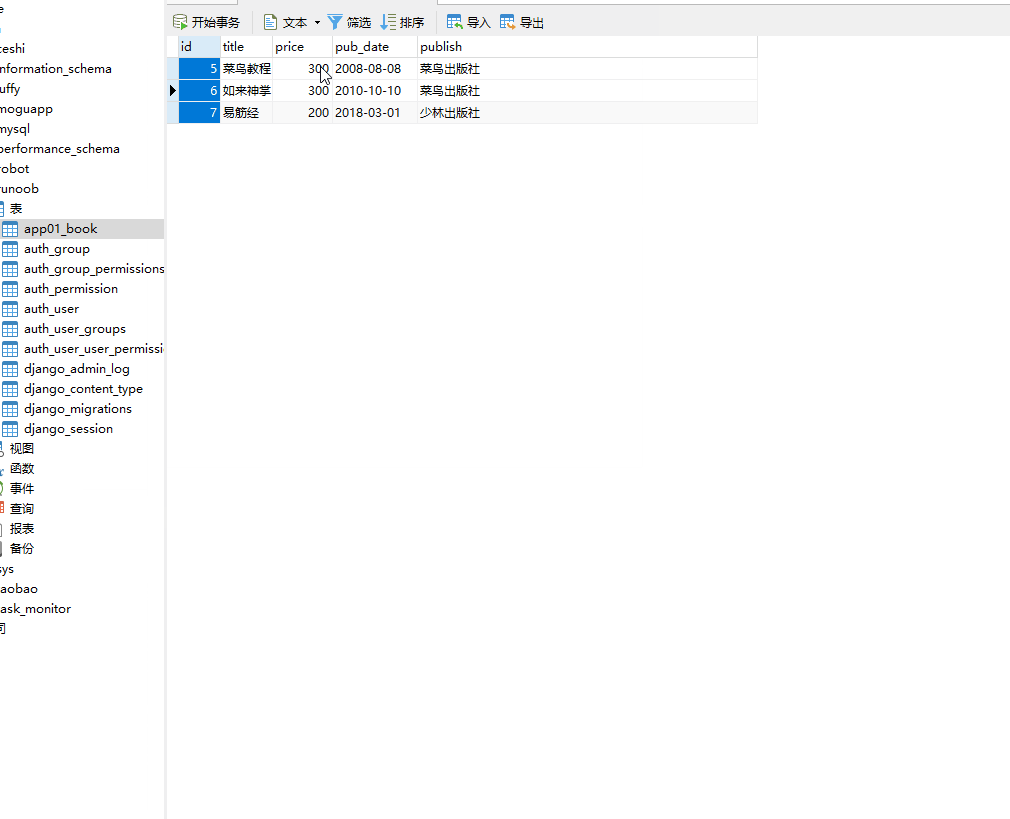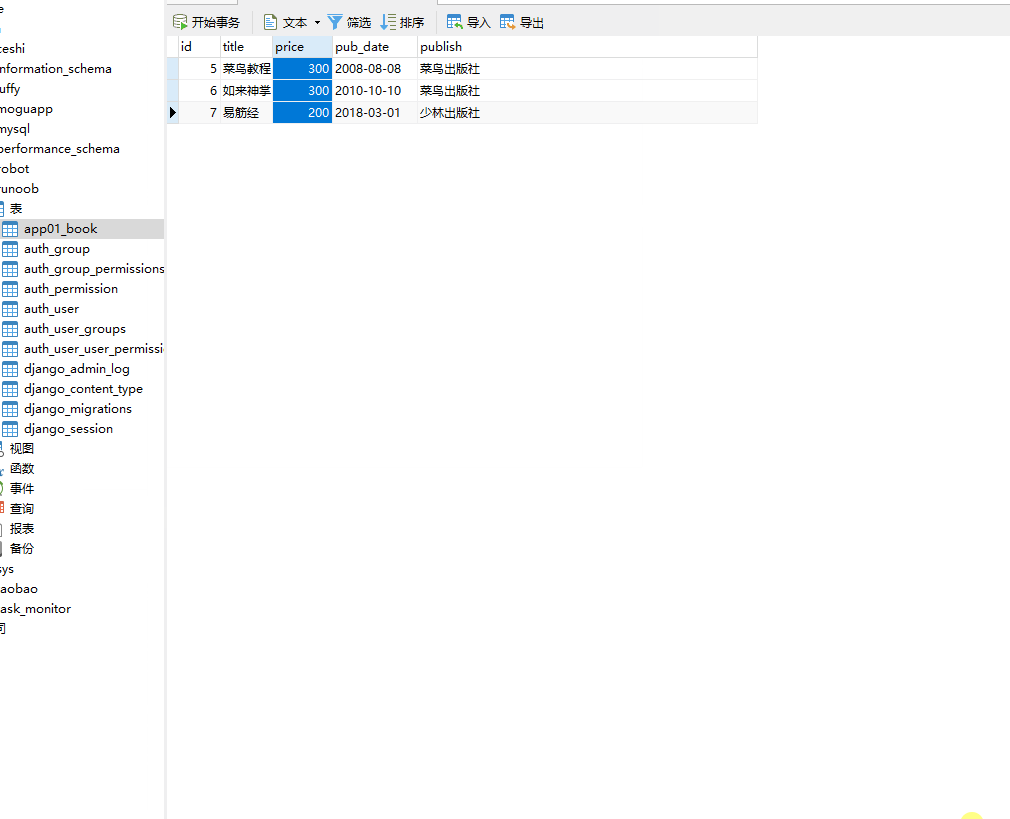
books = models.Book.objects.filter(price__gt=200)