The MySQL database uses SQL SELECT statements to query data.
You can query the data in the database from the mysql > command prompt window, or query the data through the PHP script. The following is the common SELECT syntax for querying data in an MySQL database: You can use one or more tables in the query, split the tables with a comma (,), and use the The SELECT command can read one or more records. You can use an asterisk (*) instead of other fields, and the SELECT statement returns all the field data of the table You can use the WHERE statement to include any condition. You can use the LIMIT property to set the number of records returned. You can specify the data offset to start the query with the SELECT statement through OFFSET. The offset is 0 by default. For the following example, we will get the MySQL data table through the SQL SELECT command The following example returns a data table Read the data table: Output result:Grammar ¶
SELECT column_name,column_name
FROM table_name
[WHERE Clause]
[LIMIT N][ OFFSET M]
WHERE
Statement to set the query conditions.Get data from the command prompt ¶
runoob_tbl
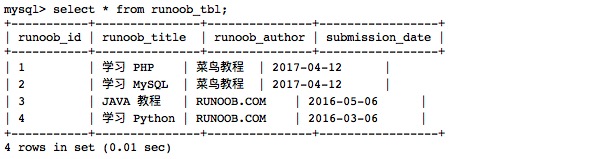
Data of:Example ¶
runoob_tbl
All records of:select\*fromrunoob_tbl;