Command pattern (Command Pattern) is a data-driven design pattern, which belongs to behavioral pattern. The request is wrapped in the object in the form of a command and passed to the calling object. The calling object finds the appropriate object that can process the command, and passes the command to the corresponding object, which executes the command. 意图: Encapsulate a request into an object so that you can parameterize the customer with different requests. 主要解决: In software systems, there is usually a tightly coupled relationship between behavior requesters and behavior implementers, but in some situations, such as the need to record, undo or redo behavior, transactions and other processing, this tightly coupled design that can not resist changes is not appropriate. 何时使用: In some situations, such as “recording, undoing / redoing, transactions” and so on, the tight coupling that cannot resist change is not appropriate. In this case, how to decouple the “behavior requester” from the “behavior implementer”? By abstracting a group of behaviors into objects, the loose coupling between the two can be realized. 如何解决: The caller invokes the recipient to execute the command, in the order that the caller → commands → the recipient. 关键代码: Define three roles: 1, received real command execution object 2, Command 3, invoker uses the entry of the command object 应用实例: There is only one action core controller ActionServlet in struts 1, which is equivalent to Invoker, and the class of the model layer will have different model classes according to different applications, which is equivalent to the concrete Command. 优点: 1. The coupling degree of the system is reduced. 2. New commands can be easily added to the system. 缺点: Using command mode may result in some systems having too many specific command classes. 使用场景: Command mode can be used wherever you think it is a command, for example: 1. Every button in GUI is a command. 2. Simulate CMD. 注意事项: The system needs to support command undo (Undo) operation and restore (Redo) operation, you can also consider using command mode, see the extension of command mode. Schematic diagram of command mode structure: Let’s first create an interface as a command Order And then create the Stock Class. Entity command class BuyStock And SellStock Has been realized Order Interface, the actual command processing will be performed. Create a class as a calling object Broker Which accepts orders and can place orders Broker Object uses command mode to determine which object executes which command based on the type of command. CommandPatternDemo Class usage Broker Class to demonstrate command mode. Create a command interface. Create a request class. Create and implement the Order The entity class of the interface. Create a command call class. Use the Broker class to accept and execute commands. Execute the program and output the result: 6.17.1. Introduction ¶
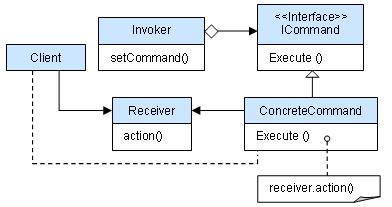
6.17.2. Realize ¶
6.17.3. Step 1 ¶
Order.java ¶
publicinterfaceOrder{voidexecute();}
6.17.4. Step 2 ¶
Stock.java ¶
publicclassStock{privateStringname="ABC";privateintquantity=10;publicvoidbuy(){System.out.println("Stock
[ Name:"+name+", Quantity:"+quantity+"]
bought");}publicvoidsell(){System.out.println("Stock [ Name:"+name+",
Quantity:"+quantity+"] sold");}}
6.17.5. Step 3 ¶
BuyStock.java ¶
publicclassBuyStockimplementsOrder{privateStockabcStock;publicBuyStock(StockabcStock){this.abcStock=abcStock;}publicvoidexecute(){abcStock.buy();}}
SellStock.java ¶
publicclassSellStockimplementsOrder{privateStockabcStock;publicSellStock(StockabcStock){this.abcStock=abcStock;}publicvoidexecute(){abcStock.sell();}}
6.17.6. Step 4 ¶
Broker.java ¶
importjava.util.ArrayList;importjava.util.List;publicclassBroker{privateList<Order>orderList=newArrayList<Order>();publicvoidtakeOrder(Orderorder){orderList.add(order);}publicvoidplaceOrders(){for(Orderorder:orderList){order.execute();}orderList.clear();}}
6.17.7. Step 5 ¶
CommandPatternDemo.java ¶
publicclassCommandPatternDemo{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){StockabcStock=newStock();BuyStockbuyStockOrder=newBuyStock(abcStock);SellStocksellStockOrder=newSellStock(abcStock);Brokerbroker=newBroker();broker.takeOrder(buyStockOrder);broker.takeOrder(sellStockOrder);broker.placeOrders();}}
6.17.8. Step 6 ¶
Stock [ Name: ABC, Quantity: 10 ] bought
Stock [ Name: ABC, Quantity: 10 ] sold
