In State Pattern, the behavior of a class changes based on its state. This type of design pattern belongs to behavioral pattern.
In state mode, we create objects that represent various states and a context object whose behavior changes as the state object changes. 意图: Allows an object to change its behavior when its internal state changes, and the object appears to have modified its class. 主要解决: The behavior of an object depends on its state (properties), and its related behavior can be changed according to its state change. 何时使用: The code contains a large number of conditional statements related to the state of the object. 如何解决: Abstract all kinds of concrete state classes. 关键代码: Usually there is only one method in the interface of command mode. There are one or more methods in the interface of the state mode. Moreover, the method of implementing the class of the state pattern generally returns a value, or changes the value of the instance variable. That is, the state mode is generally related to the state of the object. The methods that implement the class have different functions, overriding the methods in the interface. State mode, like command mode, can also be used to eliminate conditional selection statements such as if…else. 应用实例: 1. Players can have normal state, abnormal state and supernormal state when playing basketball. 2. In Zeng Hou Yi chime, ‘clock is abstract interface’, ‘clock A’ is concrete state, and ‘Zeng Hou Yi chime’ is concrete environment (Context). 优点: 1. Encapsulate the conversion rules. 2. Enumerate the possible states. You need to determine the types of states before enumerating them. 3. Put all the behaviors related to a certain state into one class, and you can easily add new states. You only need to change the state of the object to change the behavior of the object. 4. Allow the state transition logic to be integrated with the state object, rather than a huge conditional statement block. 5. Multiple environment objects can share a state object, thus reducing the number of objects in the system. 缺点: 1. The use of state mode will inevitably increase the number of system classes and objects. 2. The structure and implementation of the state mode are complex, and if it is not used properly, it will lead to confusion of the program structure and code. 3. The support of the state mode to the “open and close principle” is not very good. For the state mode that can be switched, adding a new state class needs to modify the source code responsible for the state transition, otherwise it is impossible to switch to the new state. and to modify the behavior of a state class also needs to modify the source code of the corresponding class. 使用场景: 1. A scenario in which the behavior changes with the state. 2. The replacer of condition and branch statement. 注意事项: Use the state mode when the behavior is constrained by the state, and there are no more than 5 states. We will create a State Interface and implementation of the State The entity status class of the interface. Context Is a class with a certain state. StatePatternDemo Our demo class uses the Context And state objects to demonstrate the behavior changes of Context when the state changes. Create an interface. Create an entity class that implements the interface. Create Context Class. Use Context To check the current status State A change in behavior during a change. Execute the program and output the result: 6.23.1. Introduction ¶
6.23.2. Realize ¶
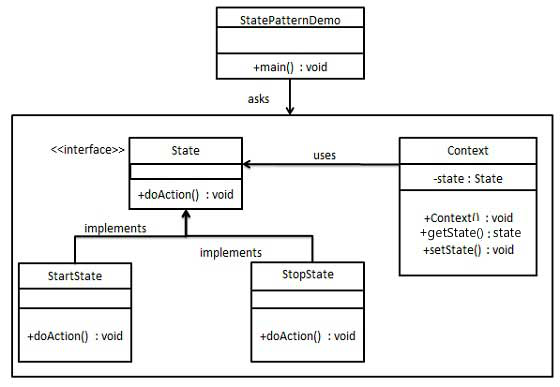
6.23.3. Step 1 ¶
State.java ¶
publicinterfaceState{publicvoiddoAction(Contextcontext);}
6.23.4. Step 2 ¶
StartState.java ¶
publicclassStartStateimplementsState{publicvoiddoAction(Contextcontext){System.out.println("Player
is in start
state");context.setState(this);}publicStringtoString(){return"Start
State";}}
StopState.java ¶
publicclassStopStateimplementsState{publicvoiddoAction(Contextcontext){System.out.println("Player
is in stop
state");context.setState(this);}publicStringtoString(){return"Stop
State";}}
6.23.5. Step 3 ¶
Context.java ¶
publicclassContext{privateStatestate;publicContext(){state=null;}publicvoidsetState(Statestate){this.state=state;}publicStategetState(){returnstate;}}
6.23.6. Step 4 ¶
StatePatternDemo.java ¶
publicclassStatePatternDemo{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){Contextcontext=newContext();StartStatestartState=newStartState();startState.doAction(context);System.out.println(context.getState().toString());StopStatestopState=newStopState();stopState.doAction(context);System.out.println(context.getState().toString());}}
6.23.7. Step 5 ¶
Player is in start state
Start State
Player is in stop state
Stop State
6.23.8. More articles ¶